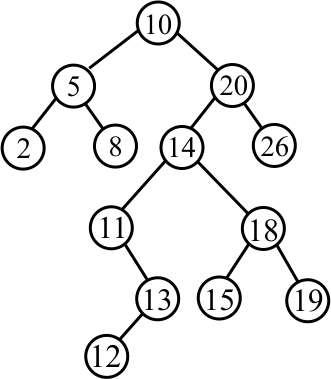
To insert a value, just find where that value would have been, had it already been in the tree, then add the value as a new leaf. For example, inserting 13 as shown below would result in the following change.

The actual insertion takes place when a null tree is encountered. The null tree is replaced by a leaf. If the value to be inserted is already in the tree, nothing is done.
//==========================================
// insert
//==========================================
// insert(x,T) inserts x (destructively) into
// binary search tree T. If x is already a
// member of T, it does nothing.
//==========================================
void insert(int x, Tree& T)
{
if(T == NULL)
{
T = new Node(x, NULL, NULL);
}
else if(x < T->item)
{
insert(x, T->left);
}
else if(x > T->item)
{
insert(x, T->right);
}
}
Notice that parameter T is passed by reference. The first case needs to change the pointer that is stored in T. Also notice that there is no case for x = T->item since insert is supposed to do nothing when x already occurs in the tree.
If x occurs at the root of T and one of the subtrees of the root is empty, then removing x is easy. Just replace the tree by the one that is not empty.

The same idea works even if both subtrees are empty. After finding that the left subtree is empty, replace T by its right subtree, whether that is empty or not. Also, a similar idea works even when the value to be removed is not at the root, as long as at least one of its subtrees is empty. For example, here is how to remove a value from a subtree, where the left subtree of that subtree is empty.

Removing a value where both subtrees are nonempty is more involved. First, we remove the smallest value s from the right subtree, then replace the value that is supposed to removed by s.

Removing the smallest value is a matter of going to the left as far as possible. Then remove the node that is found there, replacing it by its right subtree. Here is an example.
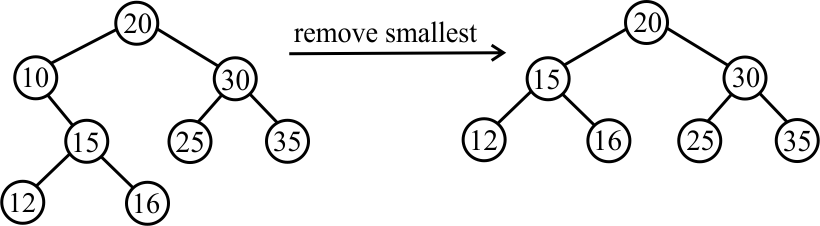
Here are definitions of remove and removeSmallest.
//====================================================
// removeSmallest
//====================================================
// removeSmallest(T) removes the smallest value from
// binary search tree T and returns the value that
// was removed.
//
// Requirement: T must not be an empty tree.
//====================================================
int removeSmallest(Tree& T)
{
if(T->left == NULL)
{
int result = T->item;
Tree p = T;
T = T->right;
delete p;
return result;
}
else
{
return removeSmallest(T->left);
}
}
//====================================================
// remove
//====================================================
// remove(x,T) removes x from binary search tree T.
// If x is not in T, it does nothing.
//====================================================
void remove(const int x, Tree& T)
{
if(T != NULL)
{
if(x < T->item)
{
remove(x, T->left);
}
else if(x > T->item)
{
remove(x, T->right);
}
else if(T->left == NULL)
{
Tree p = T;
T = T->right;
delete p;
}
else if(T->right == NULL)
{
Tree p = T;
T = T->left;
delete p;
}
else {
T->item = removeSmallest(T->right);
}
}
}
What tree do you get if you insert 25 into the following binary search tree?

What tree do you get if you insert 7 into the following binary search tree?

What tree do you get if you insert 11 into the following binary search tree?

What tree do you get if your remove 5 from the following binary search tree, using the algorithm described above?

What tree do you get if you remove 15 from the following binary search tree, using the algorithm described above?

What tree do you get if you remove 10 from the following binary search tree, using the algorithm described above?